What Are Hives?
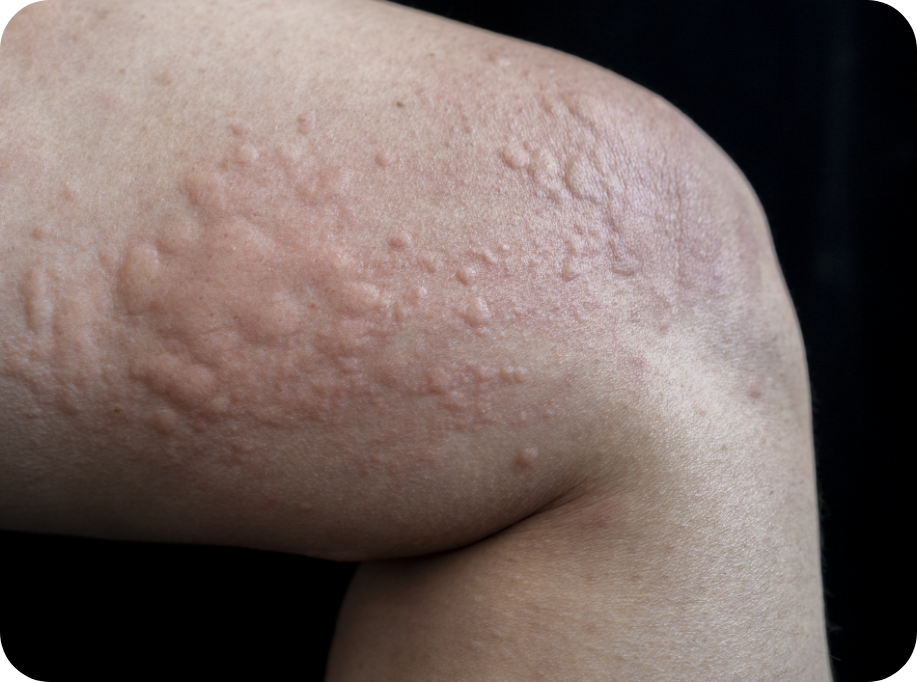
Hives, or urticaria, are raised, itchy red welts on the skin that appear suddenly. Hives can be short lived (acute) or long lasting (chronic). There are multiple possible causes of hives including allergies, infections, autoimmune conditions, thyroid disease, and blood disorders.
What Are Symptoms of Hives?
Hives are characterized by the sudden appearance of itchy, raised welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size, shape, and location on the body and are typically accompanied by several key symptoms:
Red or Pink Bumps
Development of raised, red or pink bumps on the skin that are often round or oval shaped and can range from small to several inches in diameter
Blanching
When you press the center of a hive, it tends to blanch or turn white, distinguishing it from other skin rashes
Clustered Appearance
Cluster together, forming larger welts or patches on the skin, merging and covering more extensive areas
Itching
Itching is a hallmark symptom of hives and can be mild to severe and cause significant discomfort
Transient Nature
Typically appear suddenly, and individual welts tend to come and go within hours, often relocating to different areas of the body
Angioedema
Hives may be accompanied by angioedema, which is a deeper swelling beneath the skin’s surface and cause a sense of tightness or tingling on the eyelids, lips, tongue, hands, and feet
Diagnosing & Treating Hives
Hives Testing in New Jersey
For most cases of acute hives, when there is a suspicion for an underlying infectious cause (virus or bacteria), no testing is required. In certain cases, in which a patient experiences hives that is believed to be the result of an allergy, the patient can undergo allergy skin testing or ImmunoCAP testing. If a patient suffers from chronic hives, a laboratory analysis for an underlying medical condition will be ordered.
Hives Treatment in New Jersey
How to Treat Hives
The most effective treatment for hives is eliminating or treating the underlying cause, but in some cases, medications may be necessary.
Medication Treatments
Medications used to treat acute and chronic urticaria include antihistamines, H2-Blockers, leukotriene antagonists, and steroids.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hives
Why did I develop hives? How long will they last?
The majority of cases of hives are unexplained. Allergies should be considered a cause, with paying specific attention to foods, medications and skin products. However, if there are no obvious triggers then other causes such as infections and autoimmune inflammatory reactions need to be considered.
If I am having hives does that mean I am having an allergic reaction?
Not necessarily. Hives can definitely be a sign of an allergic reaction, but they can also be a sign of something else, such as an infection or autoimmune condition.

